Simplifying scraping the web with Nannostomus
Many businesses need data from the web to fuel their analytics or drive key decisions. But raw, unstructured data found online is often messy and difficult to use. So, it was clear that companies needed a way to extract clean, usable data in a cost-effective manner, even if their teams had only basic programming skills. This led us to develop a solution for scraping the web for data.
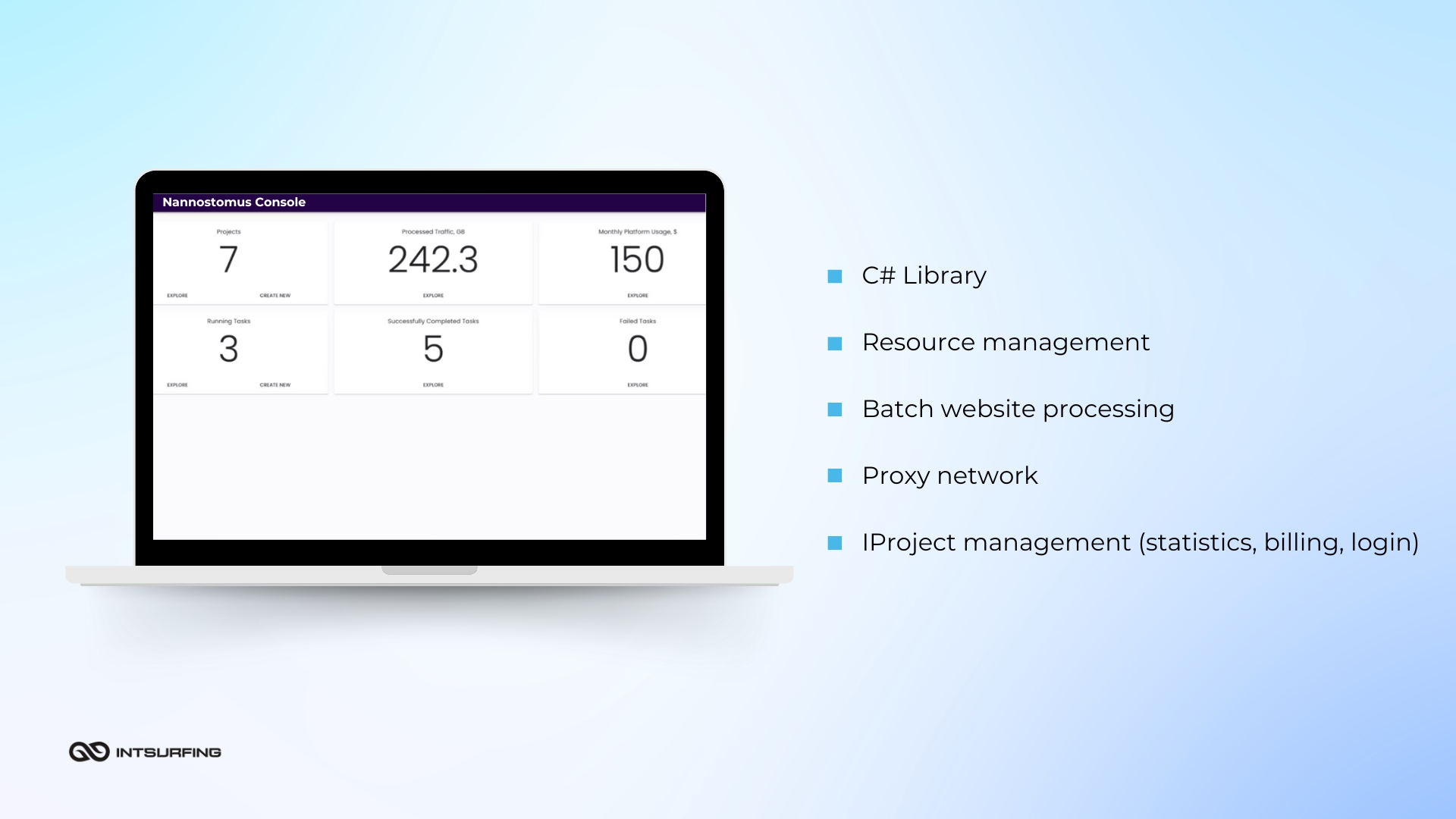
Nannostomus is a cloud-based tool with a microservices architecture. It's capable of handling 99.9% of tasks while keeping costs extremely low. For example, in one of our projects, the price of extracting a single record with images using this web scraper was $0,0001.
Challenges when building a web data scraper
Uneven load
Previous scraping setups didn’t make the best use of AWS resources. For example, due to poor organization, virtual machines were unevenly loaded. Some EC2 instances stayed underutilized while others were overworked. This imbalance led to higher costs, especially when operating at scale.
Limits
Request limits or IP bans caused by suspicious activity also made data collection tricky. To minimize the risk of getting blocked when using our web scraping software, we used proxies, rotated IP addresses, and introduced delays between requests.
High load
Another issue was the high database load when saving scraping results. When too many scrapers tried to write data simultaneously, it caused conflicts with updates to the same items. We used Optimistic Locking to manage version control, ensuring parallel writes didn’t overwrite each other.
The architecture of Nannostomus web page scraping tool
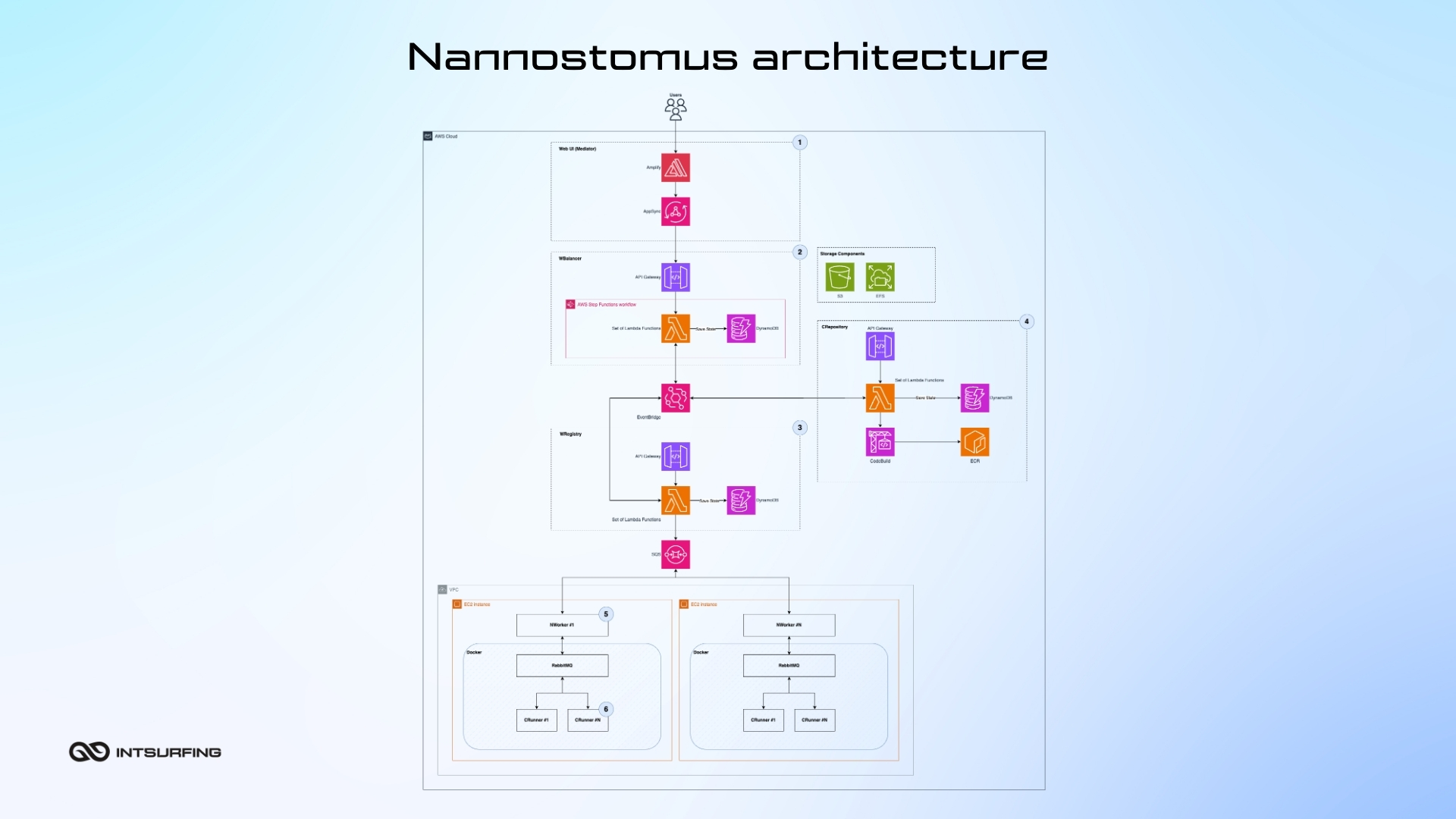
Nannostomus cloud solution for web page scraping employs a microservice architecture. This ensures you can update or repair each part of the system without disrupting the entire operation. The system has Mediator, a serverless application that interfaces between the Nannostomus Console and backend services (WBalancer for task distribution, WRegistry for worker management, and CRepository for code deployment). Nannostomus is integrated with AWS, GCP and Azure, or can be deployed on-premise.
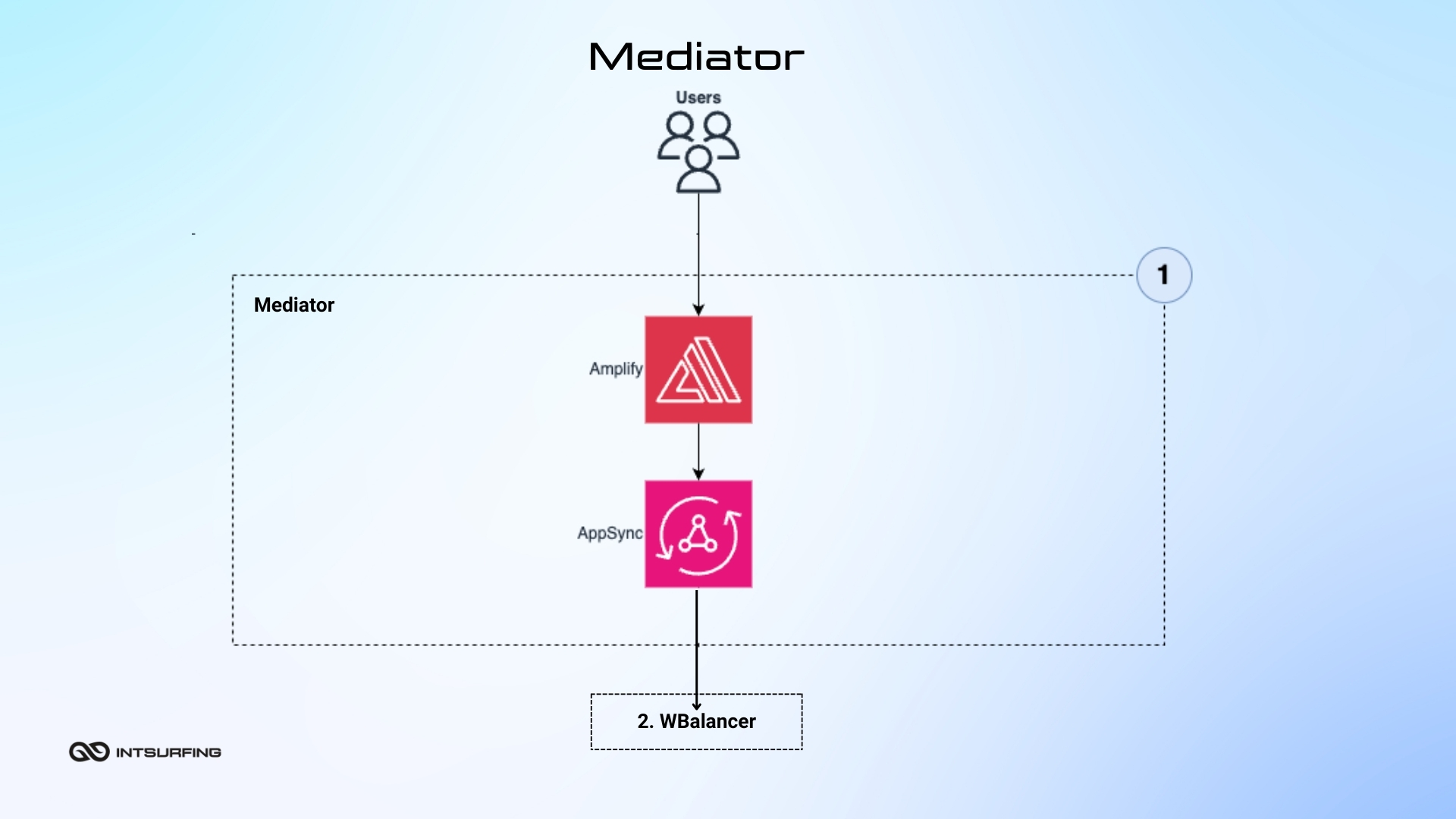
Mediator ties Nannostomus Console (the web interface you use) to backend services. When you make a request through the console, the Mediator ensures your request is passed to the right service and gets a response back. Since it`s "serverless," you don’t need to worry about managing any underlying servers. The Mediator makes things work without the need for complex infrastructure.
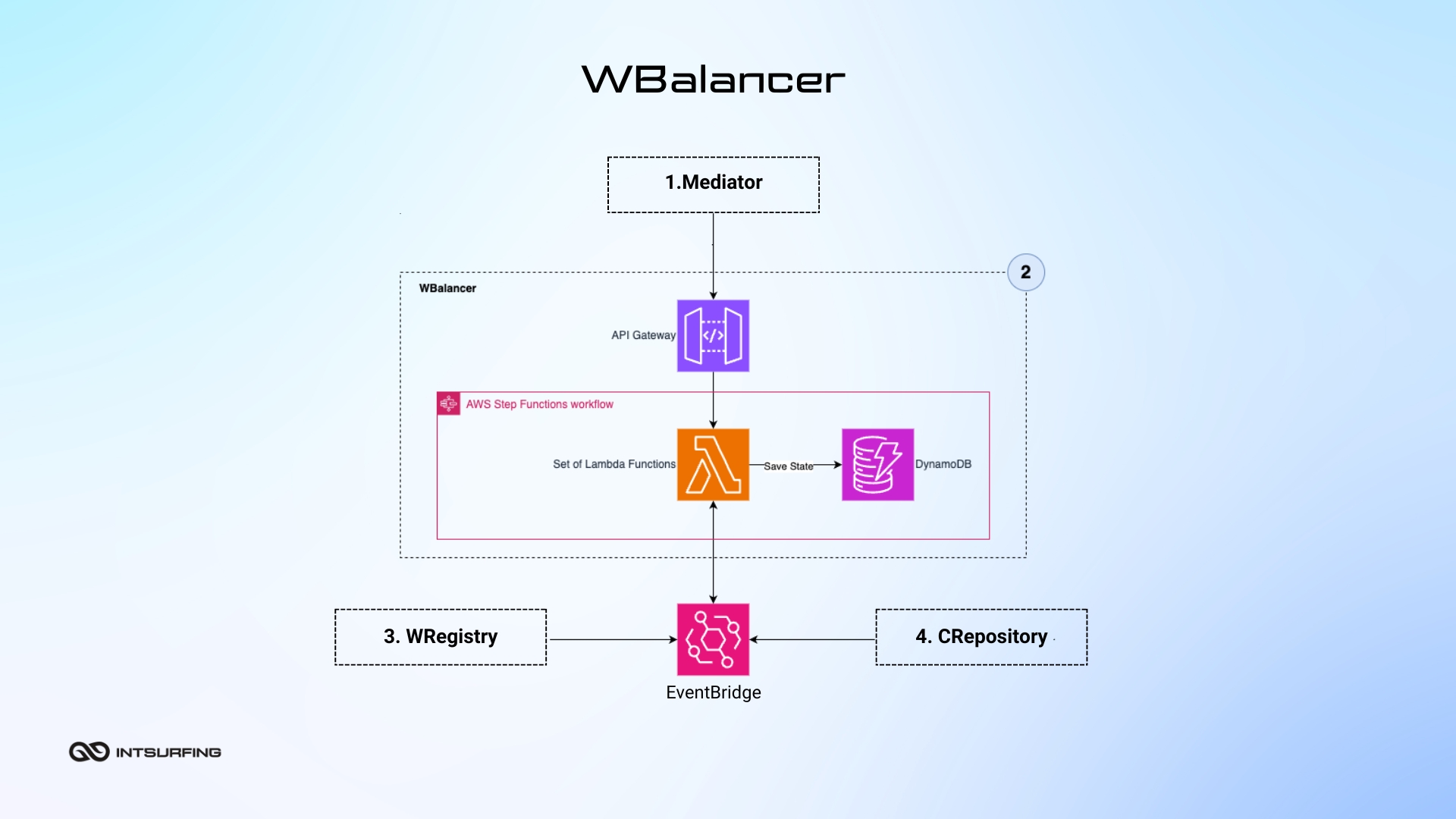
WBalancer (Work Balancer) distributes and balances all the tasks happening in the system. It looks at the available virtual machines (called NWorkers) and assigns small tasks (called chunks) to them. Thus, every machine gets just the right amount of work based on its current capacity. If a machine finishes its tasks early or starts to slow down, the WBalancer shifts the tasks around to other machines.
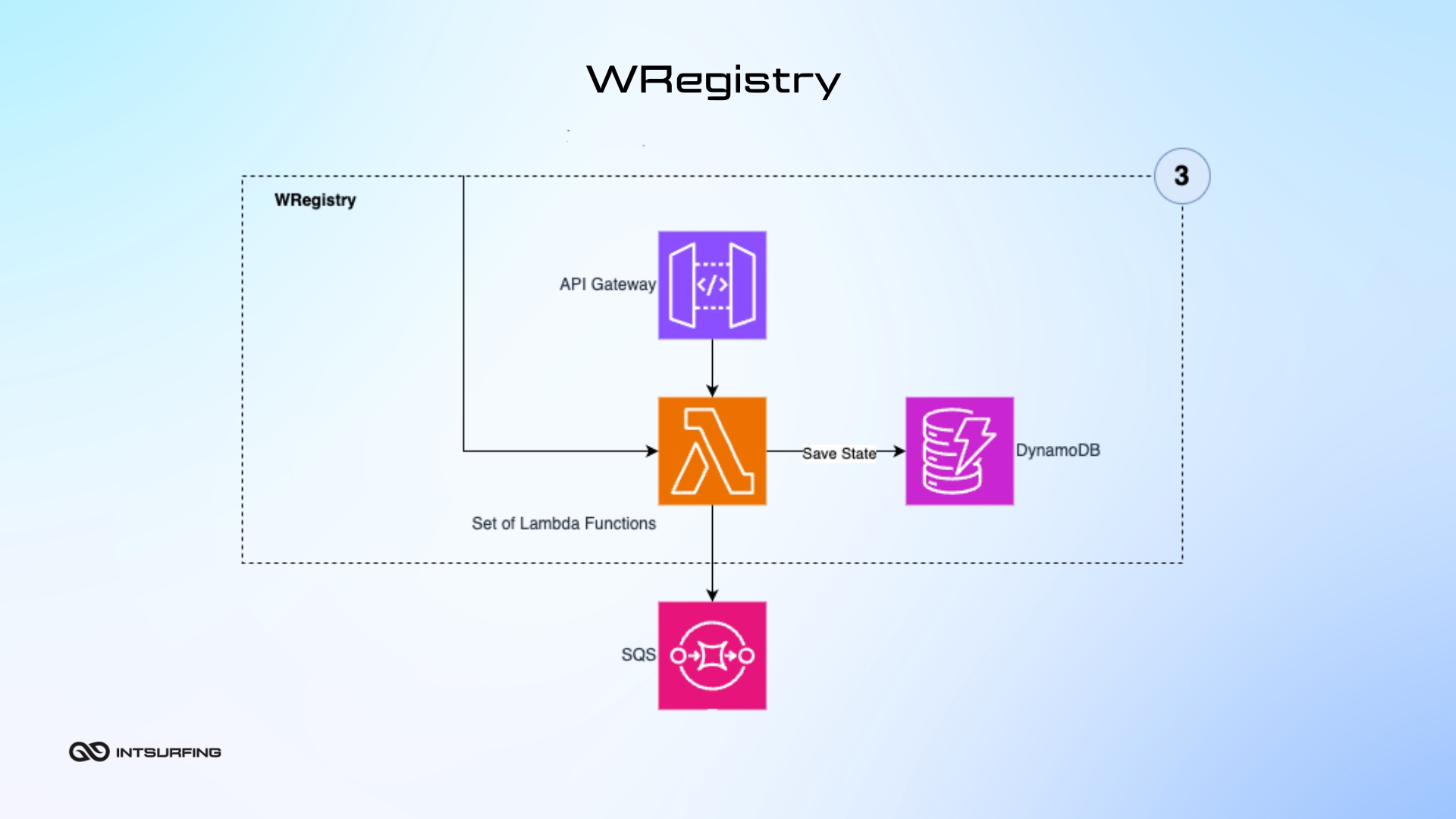
The WRegistry (Worker Registry) manages the lifecycle of NWorkers in the system. It automates the start-up, shutdown, and health checks of each NWorker so that it`s always ready to handle tasks. This continuous management helps prevent system interruptions and reduce downtime. The WRegistry guarantees that no matter the demand, our NWorkers are operational and available to tackle any job.
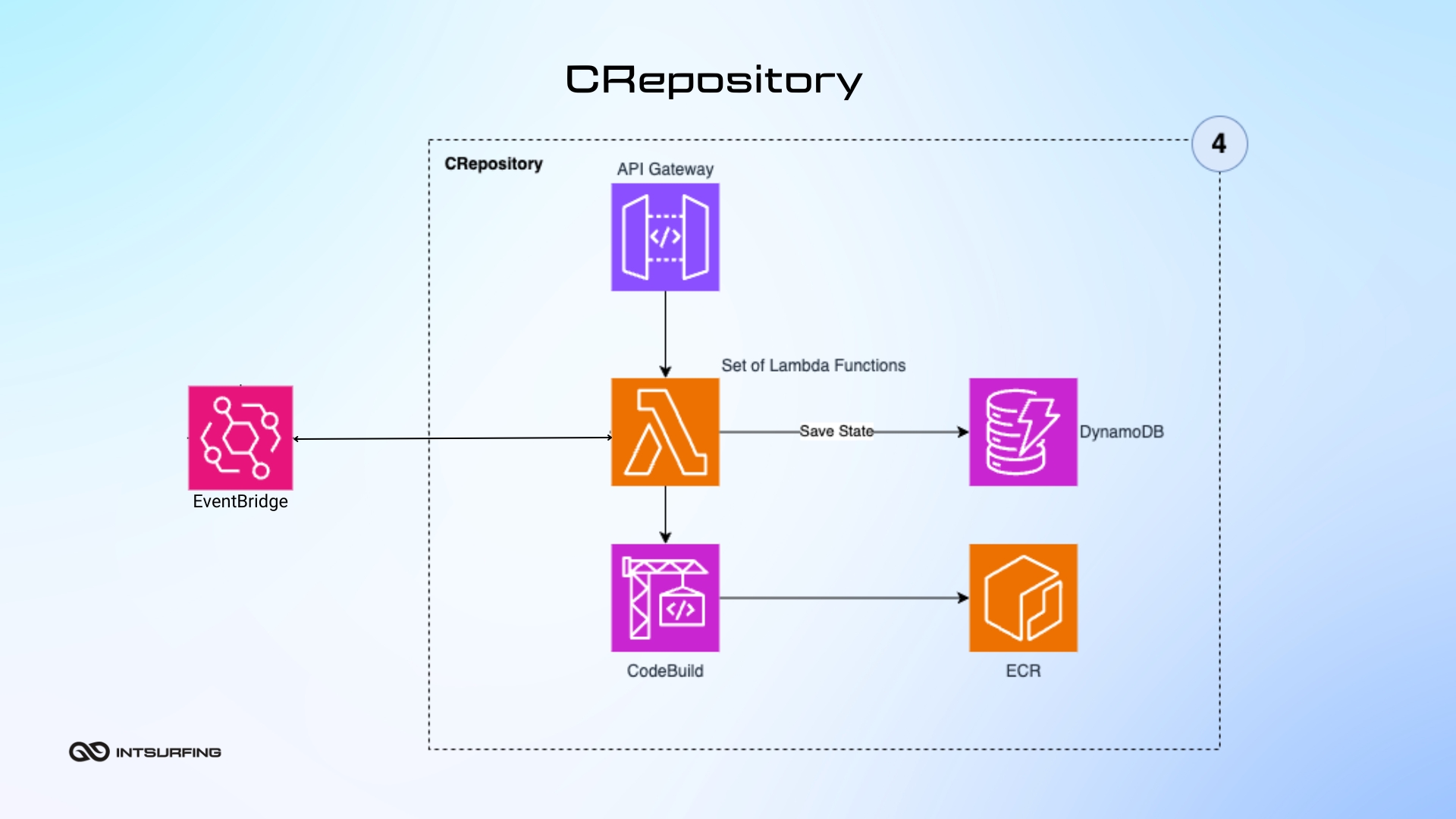
The CRepository (Code Repository) is a serverless application within the Nannostomus system where specialized software packages, called CRunner images, are built. These images perform certain tasks (like scraping web data). The CRepository takes a standard template (base CRunner image) and adds specialized modules needed for a particular job. It combines these elements to create a complete, ready-to-use software package (Docker image). Once the package is built, the CRepository sends it off to the NWorkers. It ensures every task-specific software package is correctly put together and ready to go.
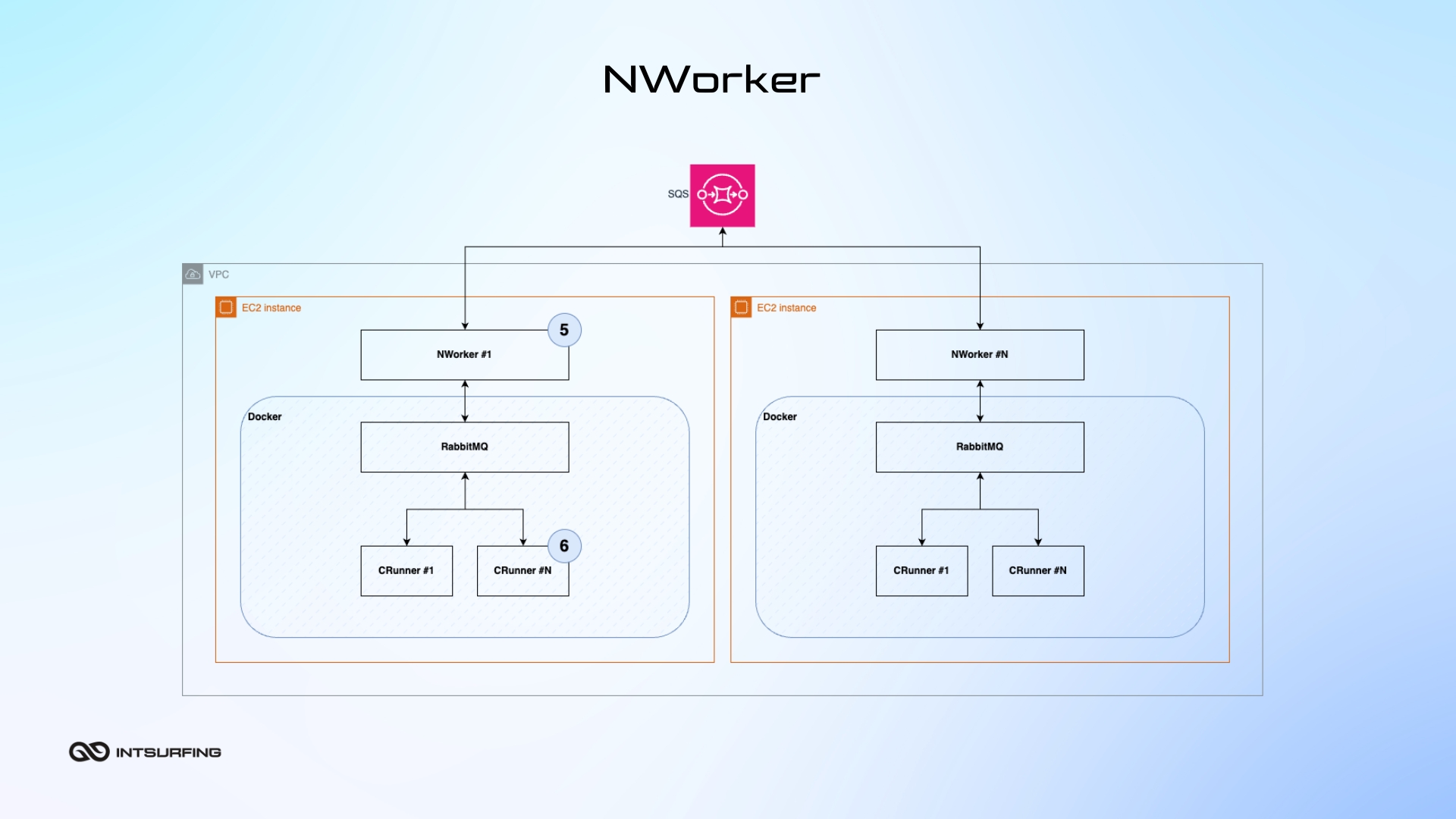
NWorker (Nannostomus Worker) is a C# application that manages smaller workers (called CRunners) inside a virtual machine. It`s in charge of starting, stopping, and checking the health of the CRunners, which are the programs that do specific tasks like scraping web pages. It makes sure that each CRunner is set up correctly and working as it should. The NWorker can manage several CRunners at the same time, all within a single virtual machine (AWS EC2 instance), allowing the system to process many tasks at once.
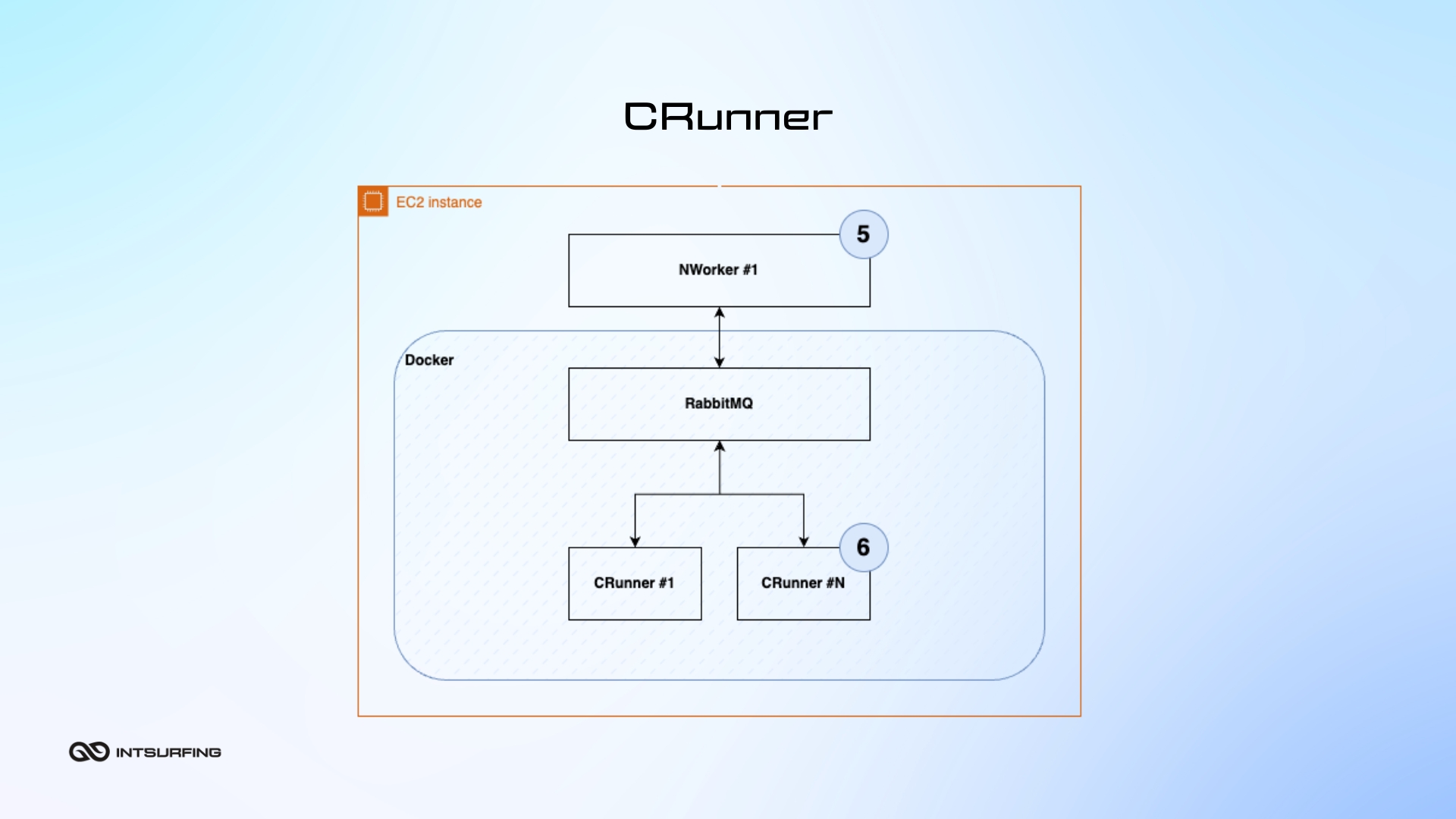
CRunner (Chunk Runner) is a C# application that takes on executing tasks. Each CRunner is given a specific job (or chunk of work) to do, like web data scraping. The NWorker supervises the CRunner to ensure it starts and runs correctly, and finishes the task without issues. For large projects, the work is divided into smaller chunks, and multiple CRunners work on these tasks at the same time. This allows the system to handle big jobs faster by processing many small pieces at once.
Technologies we used in the project

C#

Docker

RabbitMQ
AWS

Amplify

AppSync

SNS

Lambda

DynamoDB